- 2025-07-28
How to deal with salty well water?
In areas where fresh water resources are scarce, especially in rural areas, well water is a very important water source that can effectively meet people's basic living needs. However, well water generally contains various substances that may affect water quality and health. If you rely on well water for your daily life, then keep reading - this article will teach you how to remove salt and other harmful impurities from well water.
1. Introduction to borehole water
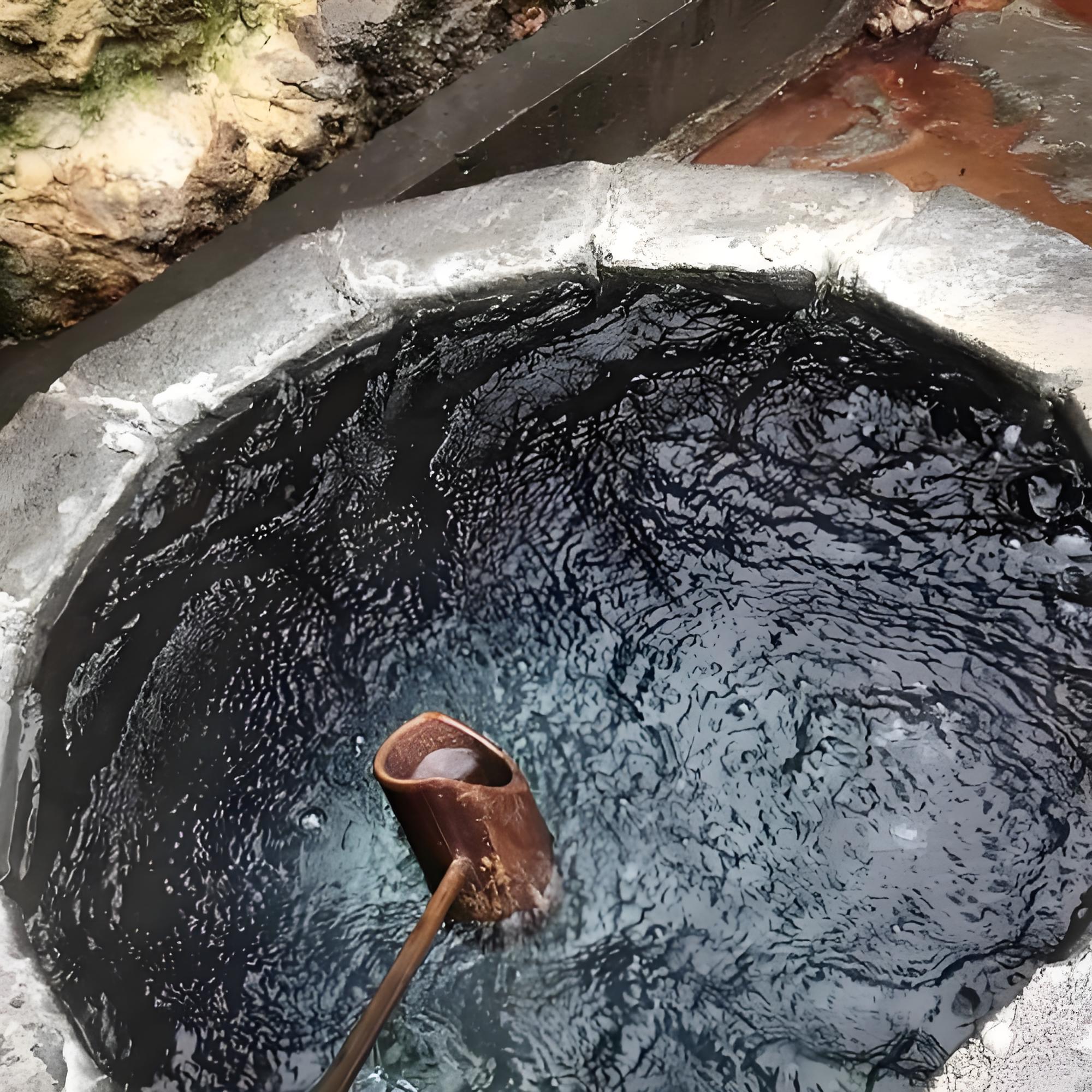
Borehole water is obtained by drilling underground with the help of mechanical equipment or manual methods to obtain groundwater resources. Surface water such as rainwater, river water, and seawater will be filtered through soil and sand and eventually converge into the borehole. Therefore, borehole water generally has a low content of organic matter and suspended particles and is relatively clear.
However, due to the depth of the well, borehole water usually contains high concentrations of minerals such as calcium, magnesium, iron, manganese, sodium, potassium, and sulfate. These minerals will affect the water quality. For example, sodium ions will make the water salty, while calcium and magnesium ions will increase the hardness of the water, thereby affecting the taste. The quality of borehole water varies from region to region, with coastal areas often having higher mineral content. In addition, rocks in the groundwater layer release heavy metals, especially in areas near industrial wastewater discharge areas and mining operations, which can increase the heavy metal content in borehole water.
2. Why is borehole water salty?
The quality of borehole water is closely related to the water source and soil environment. For example, in coastal areas, the water obtained from the borehole is almost seawater. Seawater can seep into or otherwise enter the groundwater layer, increasing the salt content of the groundwater in the area. In addition, the soil itself is rich in minerals, which mainly come from rock weathering. When groundwater flows through the soil layer, it naturally carries salts and minerals such as sodium chloride, sulfates, and carbonates, and dissolves them in the water, making the water taste salty.
The formation of salt in borehole water is also closely related to human activities. For example, excessive use of fertilizers, improper treatment of domestic and industrial wastewater, and large-scale deforestation that leads to reduced vegetation can all cause salt accumulation in the soil. These factors then increase the concentration of salt in the groundwater.
Therefore, long-term use of untreated well water may be harmful to health, may cause skin irritation, increase the burden on the kidneys, and is not suitable for drinking by patients with hypertension. In addition, the use of such well water will cause soil salt accumulation, which is not conducive to the growth of crops, is not suitable for animals to drink, and will have a negative impact on animal husbandry. In industrial production, the direct use of well water will increase equipment maintenance costs and will also have an adverse effect on the quality of the final product.
3. How to remove salt from water?
Borehole water usually has a high mineral content. Although boiling can remove a small part of the salt for drinking, it is far from meeting the hygiene standards or the requirements of industrial plants. Therefore, a more professional desalination method is needed, that is, seawater desalination:
(I) Water softener
Ion exchange filters use the ion exchange effect on the resin to replace specific salt ions and heavy metals in the borehole water. For example, common water softeners use ion exchange to remove calcium and magnesium ions.
In addition, ion exchange softeners can be designed to use specific ion exchange resins to remove heavy metal ions such as iron, manganese, lead, chromium, and specific inorganic ions. This can effectively solve the problems of high borehole water hardness, excessive content of certain heavy metals, and yellowing of water quality.
However, ion exchange filters are generally more suitable for treating low-salinity well water. If the well water contains high concentrations of sodium ions, chloride ions, sulfate ions, carbonate ions, etc., it is recommended to consider using nanofiltration and reverse osmosis filtration technology to treat it.
(II) Nanofiltration Filters
Nanofiltration technology uses a selective permeable membrane to allow water and some dissolved salts to pass through, while blocking larger salt ions, organic compounds, microorganisms and heavy metals. Compared with ion exchange technology, nanofiltration can treat more types of salt ions, such as sodium ions, chlorides, sulfates, carbonates, and some microorganisms in borehole water, thereby improving the taste and safety of water.
Unlike reverse osmosis (RO) filters, nanofiltration filters can retain some minerals that are beneficial to the human body, and usually have moderate energy consumption and water production. In addition, nanofiltration filters are efficient and inexpensive, suitable for treating low to medium salinity water sources and for partial water quality regulation.
(III) Reverse Osmosis Filter
RO filters use membrane technology to selectively allow water and certain dissolved salts to pass through, while intercepting large particles, salt ions, organic matter, microorganisms and heavy metals. Compared with ion exchange technology, RO filters can handle a wider range of salt ions in borehole water, including sodium ions, chlorides, sulfates, carbonates and some microorganisms, thereby improving the taste and safety of water.
However, reverse osmosis membranes have high requirements for water quality and usually require pre-treatment filters such as sediment filters and activated carbon filters. Therefore, the initial investment of reverse osmosis systems is relatively high, and it is suitable for users with sufficient budgets and who pay attention to drinking water quality.
4. What is the best way to remove salt from borehole water?
When deciding whether to purchase seawater desalination equipment, it is important to consider local water quality standards, personal health conditions and specific usage needs. Before purchasing, it is recommended to test the total dissolved solids (TDS) of the well water. From an economical and practical point of view, home or small water treatment systems can be tested with a conductivity meter or a salinity meter.
Conductivity is an effective way to assess the content of dissolved salts and other electrolytes in water. You can refer to the following table to make a judgment:
| Borewater conductivity (μS/cm) | Treatment recommendations |
|---|---|
| Below 500 μS/cm | Generally no desalination treatment is required |
| 500 μS/cm to 1500 μS/cm | Consider desalination according to personal preferences and needs |
| Above 1500 μS/cm | Purchase desalination equipment to ensure that water quality meets health standards and consider health issues |
For homes and small communities, we recommend considering small reverse osmosis (RO) systems. Even if the raw water quality requirements are high, these systems can effectively improve groundwater quality, effectively remove a variety of contaminants, and do not take up much space. Prices are generally between $100 and $200, depending on treatment capacity and brand, so you can choose the right product that fits your budget.
If you want to remove most soluble salts, organic compounds, and heavy metals while retaining beneficial minerals, it is recommended to consider nanofiltration (NF) treatment systems. Although the desalination effect of NF system is not as thorough as that of RO system, it has advantages in cost-effectiveness and applicability, especially for situations where water quality requirements are not strict or the raw water quality is good.
FupengWater also provides high-quality small-scale reverse osmosis (RO) systems and nanofiltration (NF) systems for medium water volume, aiming to provide affordable clean water sources for more communities and residents. You can visit our water purifier product page or contact us for professional equipment purchase advice.
5. Frequently Asked Questions
1. What chemicals can remove salt from water?
The desalination process does not rely solely on chemical agents. Chemical additives are usually used in the treatment system to treat the salt in the well water, such as scale inhibitors and membrane cleaners used to protect the performance of the reverse osmosis unit membrane. Depending on specific needs, pH adjusters can also be strategically added to improve treatment efficiency. Commonly used additives include coagulants, flocculants and bactericides.
2. How to treat borehole water naturally?
For large particles of impurities in borehole water, such as sediments, stones and suspended solids, sedimentation methods can effectively remove these insoluble substances. However, for soluble salts in borehole water, simple methods such as boiling or sand filtering without the use of chemicals or special equipment are inefficient and ineffective. Moreover, these methods may be contaminated by other impurities. Therefore, when dealing with salts in borehole water, it is recommended to consult experts and seek professional treatment methods.